Unlocking the Secrets of North America’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of North America’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of North America’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of North America’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide
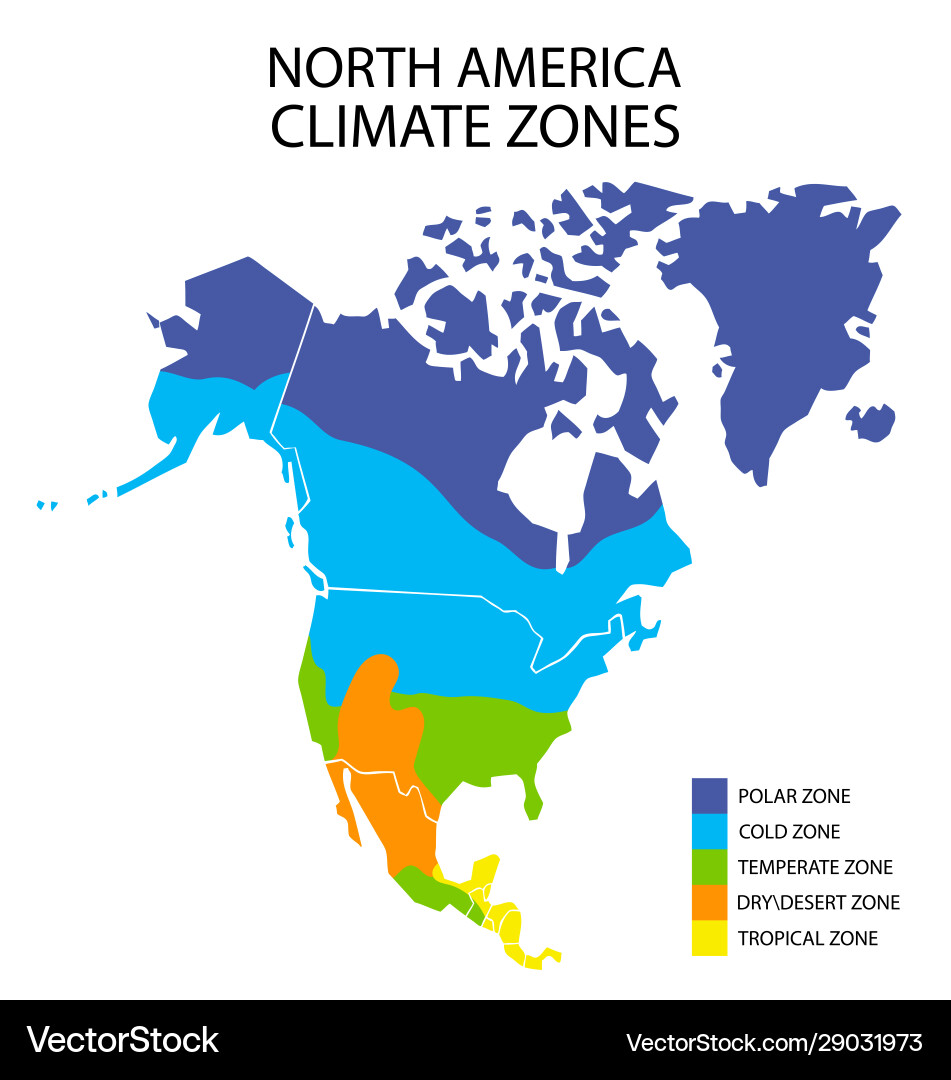
North America, a vast continent stretching from the Arctic Circle to the tropics, exhibits a remarkable diversity of climates. This diversity is a consequence of a complex interplay of factors, including latitude, altitude, proximity to oceans, and prevailing wind patterns. Understanding the climate of North America is crucial for comprehending the continent’s ecosystems, natural resources, and human settlements.
A Tapestry of Climates:
The climate of North America can be broadly categorized into several distinct zones, each characterized by specific temperature and precipitation patterns.
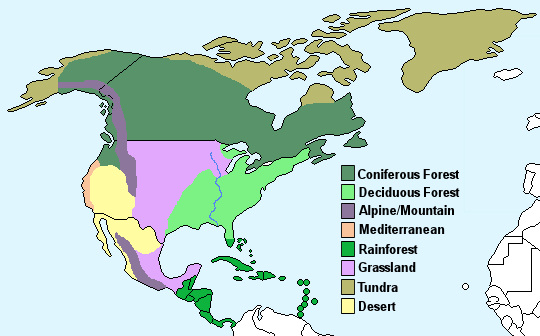
- Arctic and Subarctic: Dominated by extremely cold temperatures and limited precipitation, these regions are characterized by permafrost, vast tundra landscapes, and short, cool summers.
- Humid Continental: Located in the interior of North America, this climate zone experiences significant temperature fluctuations between hot summers and cold winters. Precipitation is generally well-distributed throughout the year, with snow being a prominent feature in the winter months.
- Humid Subtropical: This zone, found along the southeastern coast of the United States, is characterized by warm, humid summers and mild winters. Precipitation is abundant throughout the year, often in the form of thunderstorms.
- Mediterranean: Occurring along the western coast of North America, this climate zone enjoys warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The Mediterranean climate supports diverse vegetation, including chaparral and woodlands.
- Dry: Arid and semi-arid climates dominate the western interior of North America, with low precipitation and significant temperature variations. Desert landscapes and grasslands are common features of this zone.
- Marine West Coast: Found along the Pacific Northwest coast of North America, this climate zone is characterized by mild temperatures, abundant precipitation, and frequent fog. This region is renowned for its lush forests and temperate rainforests.
Visualizing the Climate Mosaic:
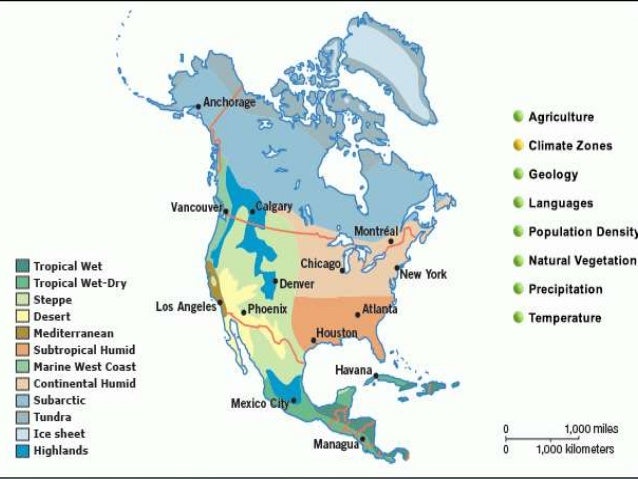
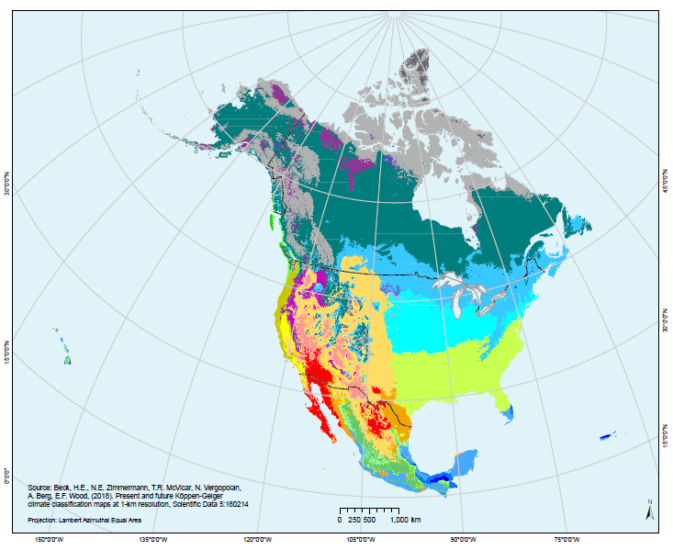
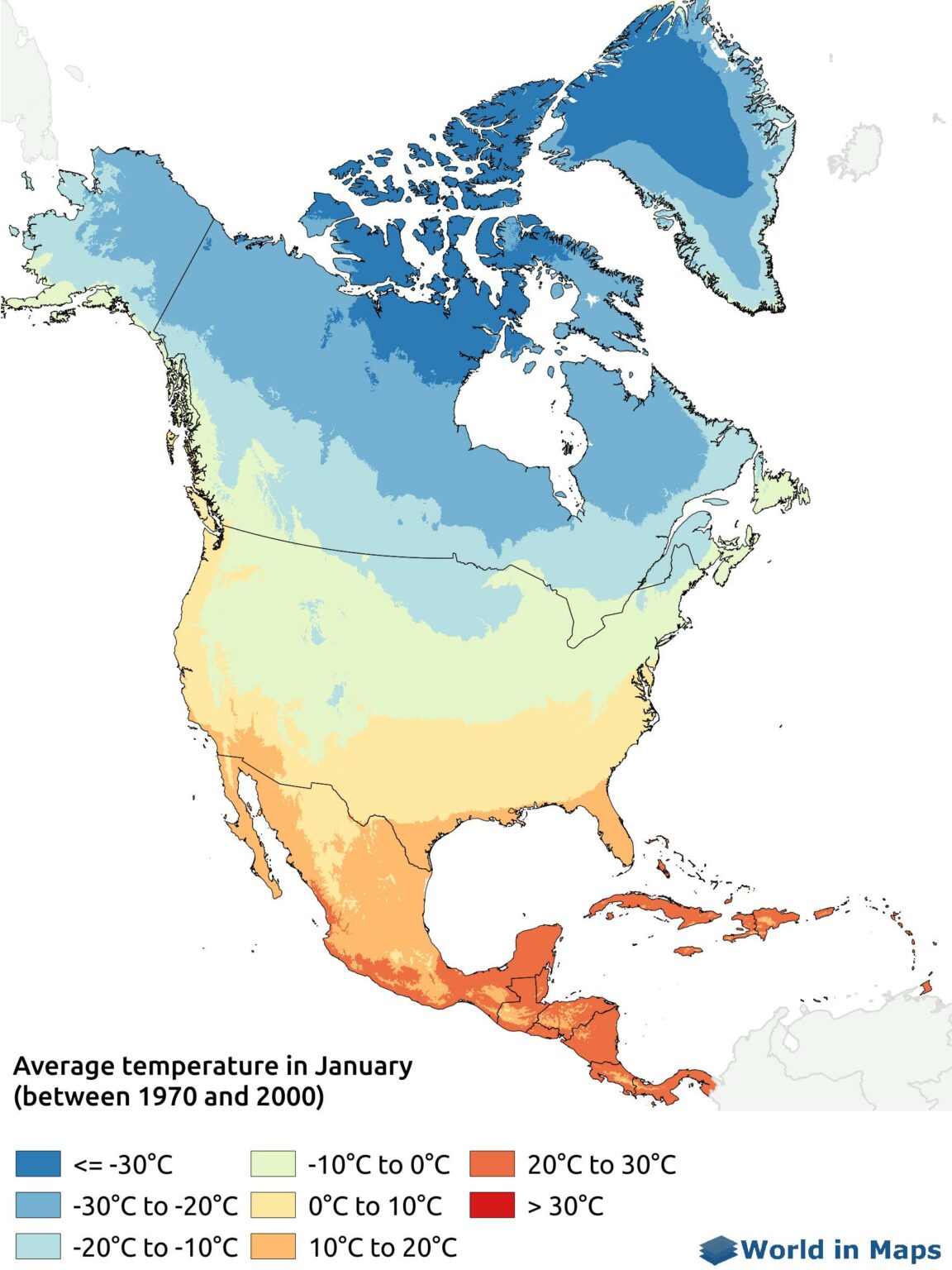
Climate maps are indispensable tools for visualizing the distribution of different climate zones across North America. These maps typically use color gradients or symbols to represent temperature, precipitation, and other climate variables.
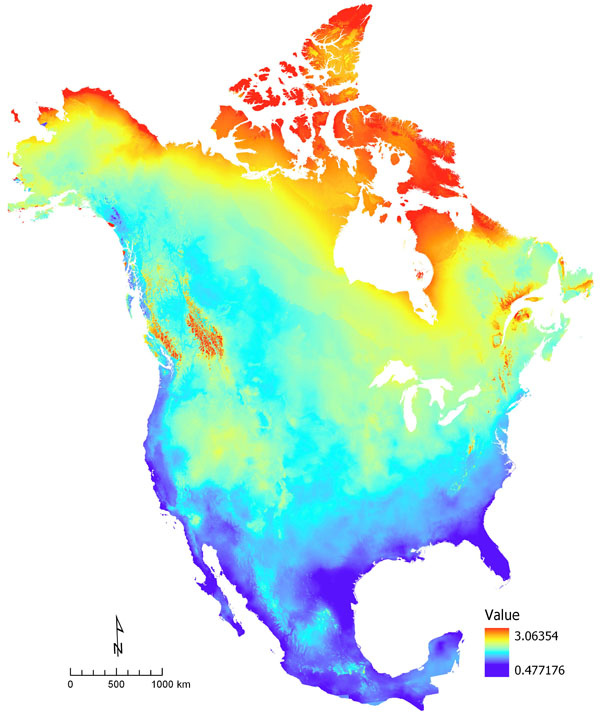
- Temperature Maps: Display the average monthly or annual temperature across the continent. Warmer temperatures are often depicted in shades of red, while colder temperatures are shown in shades of blue.
- Precipitation Maps: Illustrate the average annual rainfall or snowfall. Regions with high precipitation are often represented in shades of green, while drier areas are depicted in shades of brown.
- Köppen Climate Classification Maps: Employ a standardized system developed by Wladimir Köppen to classify climates based on temperature and precipitation patterns. Each climate type is represented by a unique letter code.
Understanding the Importance of Climate:
The climate of North America plays a critical role in shaping the continent’s natural environment and human societies.
- Ecosystem Dynamics: Climate directly influences the distribution and abundance of plant and animal life. Different climate zones support unique ecosystems, from the boreal forests of Canada to the deserts of the Southwest.
- Resource Availability: Climate affects the availability of water, soil fertility, and other natural resources. For example, arid regions face water scarcity, while humid regions often experience flooding.
- Human Settlements: Climate shapes the patterns of human settlement and economic activity. Regions with favorable climates, such as the Pacific Northwest and the Great Lakes region, tend to have higher population densities and more developed economies.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is already having a significant impact on North America, leading to more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and changes in agricultural productivity. Understanding the current climate and its projected changes is essential for adapting to these challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: How does altitude affect climate in North America?
A: Altitude plays a significant role in shaping climate. As altitude increases, temperatures generally decrease, leading to colder climates at higher elevations. This phenomenon is known as the lapse rate.
Q: What are the major factors that contribute to the diversity of climates in North America?
A: Latitude, altitude, proximity to oceans, and prevailing wind patterns are the primary factors driving climate diversity.
Q: How do climate maps help us understand the environment and human activities?
A: Climate maps provide a visual representation of climate zones and their spatial distribution, enabling us to understand the relationship between climate and ecosystems, natural resources, and human settlements.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with climate change in North America?
A: Climate change poses significant challenges, including more frequent and intense heat waves, droughts, floods, wildfires, and rising sea levels.
Tips for Using Climate Maps:
- Pay attention to the map’s legend: The legend explains the symbols, colors, and other visual cues used to represent climate data.
- Consider the scale of the map: Maps with larger scales provide more detailed information about local climate variations.
- Compare different climate maps: Comparing maps showing temperature, precipitation, and other variables can provide a more comprehensive understanding of climate patterns.
Conclusion:
The climate of North America is a complex and dynamic system that influences the continent’s natural environment, human societies, and economic activities. Understanding the distribution of different climate zones, the factors that drive climate variations, and the impacts of climate change is crucial for sustainable development and adaptation. Climate maps serve as invaluable tools for visualizing and analyzing climate data, providing insights into the intricate relationship between climate and the environment.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/NorthAmerica-5c673ef246e0fb0001319ae2.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of North America’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!